Function and working principle of vacuum pump
Function and working principle of vacuum pump
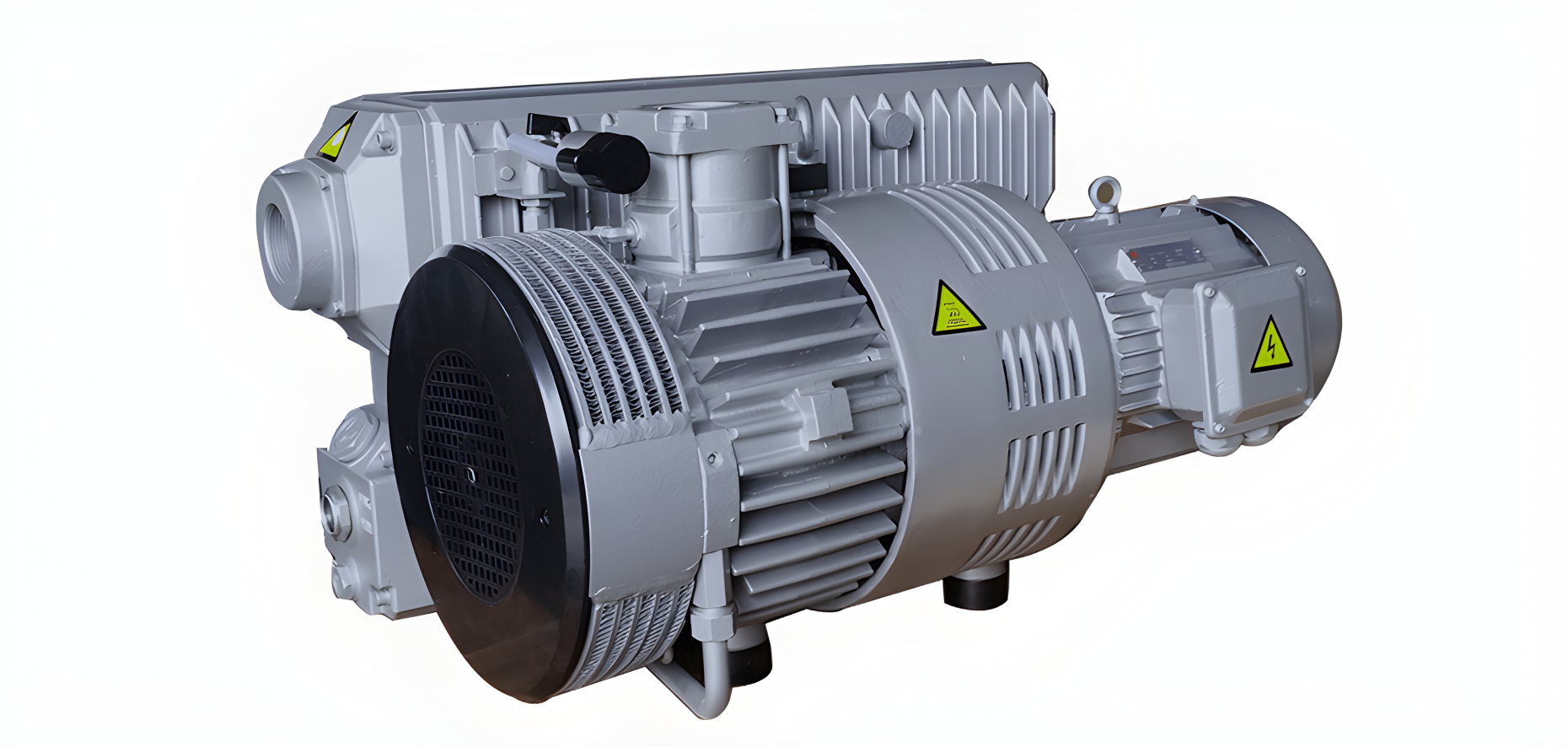
A vacuum pump is a gas conveying machine those extracts gas from a container through mechanical, physical, chemical or physicochemical methods to create and maintain a vacuum environment. Its core function is to remove gas molecules from the vacuum chamber and reduce the pressure in the equipment to the required vacuum degree. With the advancement of science and technology, the types of vacuum pumps are increasing, and the pumping speed ranges from a few tenths of a liter per second to hundreds of thousands or even millions of liters per second, and the ultimate pressure covers a wide range from rough vacuum to extremely high vacuum.
In chemical production, the application of vacuum pumps is particularly critical, and they can create the required vacuum conditions during various process operations. For example, vacuum pumps can accelerate the filtration of solutions, reduce distillation temperatures to avoid coking and decomposition, improve the efficiency of drying solids, and enhance the heat transfer effect of heat pipe heat exchangers. Due to the different requirements for vacuum degrees in different industries and applications, there are also many types and performances of vacuum pumps, including dry screw vacuum pumps, water ring pumps, reciprocating pumps, sliding valve pumps, rotary vane pumps, Roots pumps and diffusion pumps.
The overall structure and transmission mode of the vacuum pump have an important impact on its performance and service life. The vertical structure is easy to assemble and connect pipelines, but the stability is poor; the horizontal structure has a lower center of gravity and better stability. The transmission method of the vacuum pump usually uses high-precision gears to achieve the synchronous operation of the two rotors. Different types of vacuum pumps also have their own unique working principles. For example, the water ring vacuum pump uses the interaction between the water ring and the impeller to pump air, and the rotary vane vacuum pump achieves the pumping function through the rotation of the rotary vane.
When choosing a vacuum pump, they is necessary to determine the appropriate type based on the required pumping efficiency. General water pumps are suitable for rough vacuum, oil pumps can achieve sub-high vacuum, and diffusion pumps can achieve high vacuum. In addition, factors such as the structure of the vacuum pump, water pressure, vacuum efficiency, and the minimum pressure those can be pumped need to be considered. When using a vacuum pump, they is also necessary to pay attention to protecting its mechanical structure and the quality of the oil to avoid extracting corrosive or volatile gases to extend its service life.




